As educators, we understand that the classroom environment plays a key role in student success. But have you ever considered how your seating arrangements might be affecting your students' relationships, sense of belonging, and behavior? Research on social-emotional learning (casel.org) shows that a student's ability to learn is deeply connected to the environment around them.
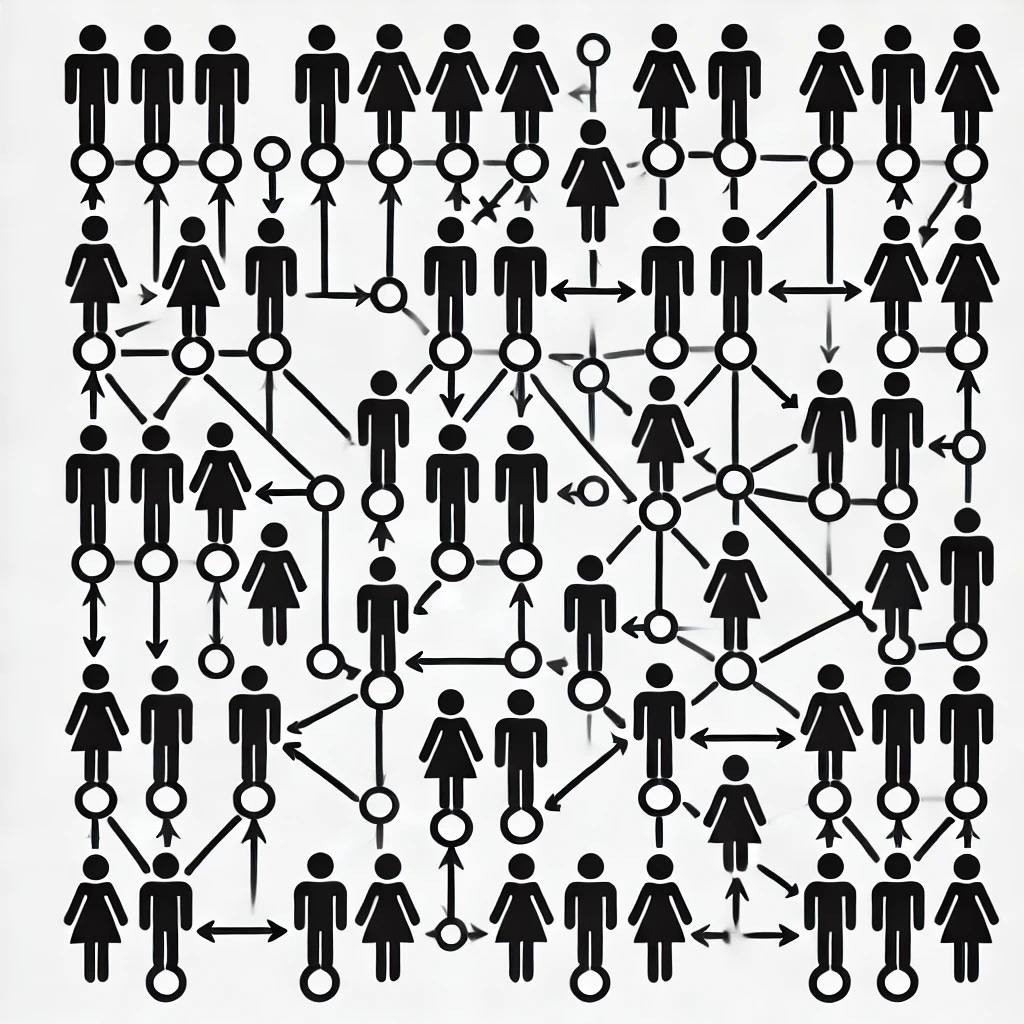
Enter the sociogram: a visual representation that maps out the social connections within your class. By using this simple tool, you can unlock key insights into group dynamics and make more informed instructional decisions.
What Can a Sociogram Tell You?
Who interacts with whom: Which students work or socialize together most often?
Social structure: Are certain students isolated, or are there group leaders influencing others?
Social roles: Who takes charge in the group? Who is more withdrawn?
Why Seating Matters for Learning & Behavior
A supportive classroom environment is essential for student learning, especially when it comes to social-emotional development. Students need to feel safe and supported before they can take risks and master new skills.
A sociogram can provide a deeper understanding of how your seating chart might impact:
Group dynamics: Where are the “popular” students sitting? Does this influence behavior or interactions?
Behavioral insights: Are students with challenges isolated, or do they sit near more influential peers? Changing seating arrangements can shake things up in a positive way, encouraging fresh interactions.
The Sociogram Activity: Mapping Classroom Relationships
Start by identifying the students who are most connected in your class—these are the ones that other students tend to gravitate towards. Now, look at your seating chart:
Are these “popular” students sitting near you or are they out of sight in the back?
Does the seating arrangement highlight any patterns in behavior? Do students with challenges sit near more popular students, or are they isolated? This activity gives you a snapshot of the current social structure and can reveal potential opportunities to improve group dynamics.
Mixing Things Up: Why It’s Important
Once you have these insights, consider adjusting your seating arrangements. It’s important to mix things up, but don’t switch seats on a whim—students need time to adjust. Think of it like changing furniture in your home: it takes a little time to get used to the new arrangement. Likewise, students need time to adjust to new groupings.
Ask yourself:
Are students interacting with a variety of peers throughout the day?
How can you create more balanced seating arrangements to encourage positive interactions?
Are students with behavioral challenges seated in ways that minimize distractions and maximize support?
Causation vs. Correlation: What’s the Difference?
Keep in mind that seating arrangements are not a cure-all. Just because a student is seated next to a popular peer doesn’t mean their behavior will automatically improve. However, seating decisions can encourage positive interactions, foster a sense of belonging, and provide the support students need to thrive.
Remember, sociograms provide a snapshot of group dynamics, but other factors like socioeconomic status, personality traits, and past experiences can also influence student behavior and interactions. A sociogram is just one piece of the puzzle.
Take Action
Next time you look at your seating chart, don’t just see rows of desks—see opportunities to foster stronger connections, better behavior outcomes, and a greater sense of belonging. Use the sociogram approach to better understand your classroom dynamics, mix things up, and make informed instructional decisions. The way you seat your students can have a profound impact on their success in and out of the classroom.
What do you think? Are your seating arrangements encouraging the classroom dynamics you want to see?
Let’s discuss in the comments!
CASEL. (n.d.). What is SEL? Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional
Learning. https://www.casel.org/what-is-sel/